Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a type of inflammatory arthritis. RA disease is characterized by chronic joint inflammation (in the fingers, hands, knees, feet, for example). RA may also be called rheumatoid disease because at times rheumatoid arthritis causes systemic illness that impacts many organs of the body.In some people, the condition also can damage a wide variety of body systems, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels. 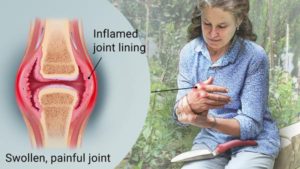
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body’s tissues are mistakenly attacked by their own immune system. The immune system contains a complex organization of cells and antibodies designed normally to “seek and destroy” invaders of the body, particularly infections. Patients with autoimmune diseases have antibodies and immune cells in their blood that target their own body tissues, where they can be associated with inflammation. While inflammation of the tissue around the joints and inflammatory arthritis are characteristic features of rheumatoid arthritis, the disease can also cause inflammation and injury in other organs in the body. Because it can affect multiple other organs of the body, rheumatoid arthritis is referred to as a systemic illness and is sometimes called rheumatoid disease. Rheumatoid arthritis is a classic rheumatic disease. Rheumatoid arthritis that begins in people under 16 years of age is referred to as juvenile idiopathic arthritis or JIA (formerly juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or JRA).
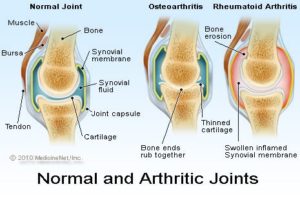
Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity.
While new types of medications have improved treatment options dramatically, severe rheumatoid arthritis can still cause physical disabilities.
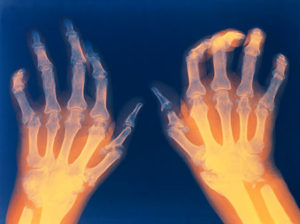
Rheumatoid-arthritis-hands